A sound processing device includes a separation unit configured to separate at least a music signal and a speech signal from a recorded audio signal, a noise suppression unit, a music feature value estimation unit, a speech recognition unit, a noise-processing confidence calculation unit, a music feature value estimation confidence calculation unit, a speech recognition confidence calculation unit, and a control unit configured to calculate at least one behavioral decision function of a speech behavioral decision function associated with speech and a music behavioral decision function associated with music based on a noise-processing confidence value, a music feature value estimation confidence value, and a speech recognition confidence value and to determine behavior corresponding to the calculated behavioral decision function.
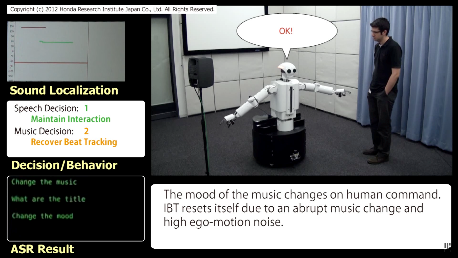
In recent years, robots such as humanoids or home robots performing social interactions with persons have actively been studied. The study of musical interaction in which a robot is allowed to hear music and is allowed to sing a song or to move its body to the music is important to allow the robot to give a natural and rich expression. In this field of technology, for example, a technique of extracting a beat interval in real time from a music signal collected by the use of a microphone and causing a robot to dance to the beat interval has been proposed (for example, see Japanese Unexamined Patent Application, First Publication No. 2010-026513). In order to allow a robot to hear speech or music, it is necessary to mount a sound collecting device such as a microphone on the robot. However, sound collected by the sound collecting device of the robot includes a variety of noise. The sound collected by the sound collecting device includes as noise, for example, a variety of sound generated by the robot itself as well as environmental sound generated around the robot. Examples of the sound generated by the robot itself include the footsteps of the robot, the operational sound of motors driven in its body, and spontaneous speech. In this way, when the S/N ratio of the collected audio signal is lowered, accuracy of speech recognition is lowered. Accordingly, a technique of improving a recognition rate of the speech recognition by controlling a robot so as to suppress the operational sound of the robot when speech is uttered by a user while the robot operates has been proposed (for example, see Japanese Patent No. 4468777).
Robots can, with this invention, correctly interpret sound to act accordingly. An example is the need to perform beat tracking when dancing or the like. For that it is necessary to reduce the influence of noise and to accurately detect beat intervals from a music signal. However, when a user speaks during the music, the speech from the user has an adverse influence on detection of the beat intervals. A music signal has an adverse influence on recognition of the speech from the user. Accordingly, there is a problem in that it is difficult for a robot to accurately give a behavioral response to the speech from the user while detecting beat intervals. The present invention is made in consideration of the above-mentioned problem and an object thereof is to provide a sound processing device, a sound processing method, and a sound processing program which can accurately detect beat intervals and accurately give a behavioral response to speech of a user even when music, speech, and noise are simultaneously input.
This invention can be very useful for real-time uses regarding Human/Robot interaction, active audition humanoids or audio control applications.






